Let's figure out what an OTA update is on Xiaomi
Today, firmware for smartphones is developing much faster than even a couple of years ago. Various innovations not only improve the experience of using a smartphone, but also give new sensations, which is very important if you are buying a phone for several years to come.
Previously, the update process could be confusing and very inconvenient for beginners, but now even a child can “roll” the latest firmware version. We can thank an update method called OTA for this.
OTA is available for almost every modern smartphone. Naturally, this update method is supported by devices from our favorite brand Xiaomi. Today we will figure out what OTA is and how to “work” with it.
OTA – what does this term mean?
In fact, OTA has been a long-standing type of update installation. The abbreviation stands for “Over The Air”, that is, “by air”.
Already from the name you can imagine the principle of OTA “working”: instead of “manually” downloading the firmware file and using recovery, the smartphone seems to catch the files necessary for it from the manufacturer’s servers and install them automatically.
This is convenient, first of all, for people who do not understand and do not want to understand the process of updating the software of their smartphone - everything is done almost offline, the person only has to start the installation process.
What is the difference between the OTA version and the Recovery version?
Many people are interested in which MIUI firmware is better: OTA or Recovery (Fastboot). There are several significant differences, namely:
- If the OTA arrives automatically, then the file size is about 500-800 MB, since only new features and changes are included in it. The firmware for Recovery is full-size, that is, it weighs 1-2 GB. Clarification: the OTA archive was downloaded from the Mi Community forum - then it will also be complete.
- A significant disadvantage of OTA firmware is the presence of errors and glitches that can affect the operation of the smartphone. Versions for Recovery and Fastboot are more stable.
- Using the OTA shell, you cannot switch from one version of Miyuai to another. But the firmware for Recovery and Fastboot allows you to change, for example, Global to EU.
- OTA updates are quick and easy. There is no need to unlock the bootloader or carry out other serious actions with the smartphone. But for flashing via Fastboot or Recovery, an active bootloader is required.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which type of firmware is better. Each user chooses the best option for themselves, based on personal preferences. We advise beginners to update via OTA, but experienced owners can try Fastboot or Recovery.
Pros of updating over the air
As we have already said, the main advantage of OTA is its convenience - the update files are downloaded by themselves. By the way, you don’t have to wait for your smartphone to connect to the Wi-Fi network – mobile Internet will also work. However, it is worth remembering that the volume of downloaded files can reach several Gigabytes - be careful.
However, in general, there is no need to worry about minor updates, since the update does not “arrive” in the form of a whole firmware file - you only receive the necessary patches and fixes, which greatly speeds up the process of installing new firmware.
The positive side of the OTA update is also the guarantee that the official software will be installed on your device directly from Xiaomi “home”. No more worrying about malicious files and viruses.
Another feature of the overall convenience of updating over the air is the lack of need to unlock the bootloader. In fact, it is this point that gives the average user confidence that he will not break his device due to his “crooked” hands.
What is an OTA update (FOTA)
OTA is an update package that comes to a Xiaomi smartphone via mobile Internet or Wi-Fi connection. The abbreviation OTA comes from the English phrase Over The Air, which means “by air”.
This is the same as FOTA (Firmware Over The Air), translated from English as “firmware over the air”.
Installing the OTA Update does not require a PC, and when installing the firmware, your data is not lost.
Any OTA package includes files that allow you to install firmware on a specific Xiaomi smartphone:
- The META INF folder contains files for performing the update.
- The Patch catalog includes improvements released by firmware developers. Thanks to this folder, system bugs are fixed.
- The System folder contains files that add new functions to the operating system, change the appearance and affect the operation of the OS.
- The check files are designed to scan the installed system and determine whether the stock MIUI from Xiaomi is installed on the phone.
- Files for checking available updates are designed to assess the degree of “freshness” of the installed OS. If the necessary updates were installed previously, not everything from the new package will be installed.
- A set of instructions determines which files need to be deleted and which should be left for stable operation of the firmware.
- Patches ( driver update kits) are designed to ensure the operation of components, for example, CPU, RAM, mobile modem.
- The instruction package determines whether a particular user has sufficient rights to install the update.
This is the standard composition of any OTA firmware.
Not every MIUI firmware version receives OTA. In some cases, developers release packages for firmware only through Recovery or Fastboot.
To choose OTA or Recovery ROM, let's look at their differences:
- Recovery can only be downloaded; this firmware does not arrive “over the air”.
- Installing Recovery ROM is done through the phone's Recovery Mode.
- Recovery weighs more because it contains full firmware for the smartphone. The OTA contains only part of the files needed for the update.
- Recovery ROM can be installed on any version of MIUI, OTA only on those specified by the developers.
- Recovery can be stock (official) and custom (from third-party developers). OTAs are official only.
Cons of OTAs
Basically, the disadvantages of updating over the air are absolutely insignificant - many may even consider them unimportant. Still, we are obliged to warn about them.
Firstly, OTA is simply not available for “craftsmen” who are accustomed to customizing a smartphone according to their specific needs (installing different firmware, root rights, and so on).
Secondly, users who have installed a new firmware version on an “old” device may notice a slowdown in the performance of their phone.
This is due to two reasons: 1) Xiaomi programmers often do not strive to optimize new functions for outdated hardware, 2) installing a new firmware version “on top” of the old one (without clearing the storage) may result in incompatibility errors.
As we can see, there are more advantages of OTA, and their weight definitely outweighs the possible disadvantages.
How does OTA work?
We said above that updating over the air makes it possible to download only those files that are currently needed to “upgrade” the firmware version. The archive itself, which “arrives” when updating your device, consists of three main components: System (the main part of the new firmware version), Patch (files that correct the “jambs” of the previous build) and META-INF (information about what will be updated ).
You don't have to worry about downloading these files and finding the path to them in Explorer - everything is done without your participation.
How to update your Xiaomi over the air?
Well, we've looked at the theory - let's move on to practice. Before starting the update, be sure to make sure that your smartphone is “ready” for this process.
Prerequisites for OTA include: a locked bootloader with stock (native) Recovery, stock firmware (not custom) and no root rights. We strongly recommend keeping your smartphone's charge at least 60 percent, and also “cleaning out” the storage so that you can download the necessary files.
Automatic update
Let's start with the most popular and easiest way to update your Xiaomi. Based on the name of the method, you can understand that the smartphone will perform all steps to update the firmware offline - you will only need to agree to fulfill some of the device’s requirements.
The beauty of automatic updating is that in most cases you will simply receive a system notification that you have received the latest firmware version. However, if you know that an update is available, but the notification never arrives, you can check for it manually.
Go to the general Settings of your smartphone and click on the “About phone” section. Inside we will find a list of subsections, among which we find the item “MIUI Version”. An update menu will open, at the bottom of which you will find a “Check for updates” button. Click on it and wait for the search to complete.
If the firmware is available for download, click on the “Download” button and wait until the update is completely downloaded. Once the download is complete, click on the “Restart” button and just wait for the installation to complete. During this time, you cannot do anything with your smartphone, otherwise there is a high chance of getting a brick.
After loading into the system, wait a couple of minutes for the firmware to “fall” into place and enjoy the update.
Manual update
If the search in Xiaomi Settings did not lead to the desired result, and the latest firmware is already on the company’s official forum, then you can install the update manually.
To do this, you need to go to the Mi Community forum, where you can always find the latest (official) builds for your device. In the site search, enter the model of your Xiaomi and go to its page. On this page, look for the “Download Full Rom” button, click on it and wait for the download to complete.
A small note: it’s better to download directly from your phone, so as not to bother with transferring the archive from your PC to your smartphone.
After downloading, we return to the already known item “MIUI Version” and click in the window that opens the icon in the form of three dots in the upper right corner of the screen. A choice of possible actions will appear - you need to click on the “Select firmware file” item.
An explorer opens in which we need to select the recently downloaded archive with our firmware update. Click “Ok” and wait for the file check to complete and the update to be installed.
By the way, the manual update option is preferable for users who want to completely get rid of the risk of getting the same errors when installing only truncated update files. This is due to the fact that from the MIUI forum you download the full version of the latest firmware from Xiaomi.
You can simplify and speed up the process of installing the full version of the update a little - for this, in the “MIUI Version” item (by clicking on the three dots) there is a “Download full firmware” sub-item. If you do not immediately find this item, click on the MIUI 12 logo several times until a message appears indicating that additional settings have become available.
After that, click on the line “Download full firmware”, wait for it to download and when finished click on “Reboot”. The installation will proceed as usual.
Additional ways to update Xiaomi
The following methods for updating your smartphone are not at all related to OTA, but we cannot help but mention them. After all, unforeseen situations often happen and the latest firmware does not install as smoothly as we would like. In this case, it makes sense to use alternative methods of installing the firmware.
Via Recovery
First, let's look at a simpler update method - through the built-in Recovery. Download the full firmware file, transfer it to the root of the repository and rename the archive to update.zip. Then turn off the phone and go into Recovery itself - to do this you need to simultaneously hold down the power button and both volume control buttons.
Once in recovery, we see a choice of several actions. We need to click on the “Install update.zip to System One” item. After this, the installation process will begin, after which click on the “Reboot to System” button to turn on your device.
Via Fastboot
The second method of flashing is relevant in the most advanced cases. For example, if your smartphone has turned into a brick after an update, or errors have appeared in the operation of the device that cannot be solved by simply flashing the smartphone itself.
To flash firmware via Fastboot we will need the Mi Flash program. Not long ago we talked in detail about working with this software, so this time we will only touch on the most important stages of the firmware.
Be sure to download the firmware version specifically for Fastboot - the standard version will not work for recovery. After unpacking, do not forget that neither the folder nor individual files can be edited. We also make sure to install all the necessary drivers. The program itself will help us with this, the main thing is to agree with all the pop-up windows.
Firmware using Mi Flash will return your Xiaomi to its original condition. That is why we use this method only in emergency cases when it is already lost.
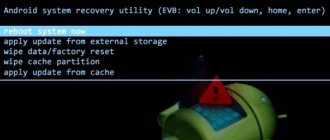
Method 1: Install the OTA update from the "Apply ZIP" recovery partition.
Note: Custom recoveries such as TWRP, CWM, PhilZ touch, etc. may not work. You will most likely need a stock recovery to install OTA updates manually.
- Download and transfer the OTA update .zip file to the internal memory of your Android device (do not put it in any folder).
- Boot your device into recovery mode . └ In recovery mode, use the Volume buttons to navigate up and down between options and the Power button to select an option.
- Select the “Apply update” or “Apply update from phone memory” option.
- Select the OTA .zip file you transferred in step 1 above. and install it.
- Once the installation is complete, select reboot from the main recovery menu.
Bonus: Why can't I see the OTA update if it's already on the forums?
The answer to this question is very simple: it’s not your turn yet. The fact is that Xiaomi sends update files piecemeal, and not to all of its devices at once. This was done in order to prevent errors from appearing on a large number of phones.
To begin with, the latest version of the firmware is sent to a limited number of smartphones to check its stability. If the company does not receive super-negative criticism, then the second and third waves of sending updates begin. If the latest firmware brings a large number of bugs, the update distribution is stopped, and programmers “finish” the newly released software.
Xiaomi is also simply afraid of overloading its servers - today there is an unimaginable number and variety of products from the Chinese brand in the world, so sending a new firmware version even for one model would be an impossible task.
Therefore, we conclude: if you don’t want to bother with additional update options, then just be patient and wait for the coveted notification about the new version of MIUI to appear.
Distribution specifics
It makes sense to focus on the examples of Xiaomi and Samsung. These firms use original policies. It includes the following steps:
- Initially, the latest firmware version is provided to testers . They check its work according to given algorithms.
- Access to the firmware for a small number of users . 1% of users registered in the relevant services receive the latest software as a control (and experimental) group. If at this stage complaints from the testing group begin to arrive, the firmware is recalled and sent for revision. If complaints are poorly substantiated (“previously the interface was 2 pixels to the left, it’s more convenient for me to return it”), more users get access to the update.
- A larger number of users are covered – approximately 25%. At this stage, some flaws come to light and quick fixes are launched (not complete rewrites like in Stage 2). However, the product has already proven itself and can be given to a large number of people. It is worth understanding that if 5% of users experience any problems, the update will be rolled back.
- Full access . By this stage, the main problems and problems have already been eliminated and the update becomes publicly available.
How to get rid of lag on Android tablets and smartphones
This process, despite the complexity of the description, takes 2-3 months . In this case, the first stage can take up to 75% of the time. Typically, the control group receives the maximum working product.